TEF is a serious complication after EA/TEF repair, with an incidence of 3–14% (2). Complex reoperation is usually required to address TEF and is associated with a high rate of complications. It is important to understand the influencing factors of TEF in order to prevent its occurrence. However, literature on factors affecting TEF is rare. In this study, we retrospectively reviewed the cohorts of patients with Gross type C EA/TEF from two tertiary children’s hospitals in China and found that surgical closure technique of original TEF and the length of initial stay could influence the occurrence of rTEF after Gross type C EA/TEF repair.
Patients with TEF usually present with choking and recurrent pneumonia. However, these symptoms may also appear due to other complications after the operation of EA/TEF, such as esophageal stricture or gastroesophageal reflux. It is difficult to diagnose TEF by symptoms alone and it is usually necessary to rely on auxiliary examinations such as bronchoscopy, esophagography, and esophageal gastroscopy to form a diagnosis (4, 5). Repairing TEF through thoracotomy or thoracoscopic surgery is the most reliable treatment, but it can also be treated using endoscopic therapies, tissue adhesives, or de-epithelializing agents (4, 5). Conservative treatment is generally required, and surgery is performed when the child’s lung infection and systemic nutritional status permit (3, 6). A systematic review reported that the probability of a second recurrence after thoracotomy repaired TEF was 21%, the incidence of postoperative leakage was 16%, and the postoperative mortality rate was 3.7% (6). Therefore, understanding the risk factors of TEF is of great significance to prevent the occurrence of TEF.
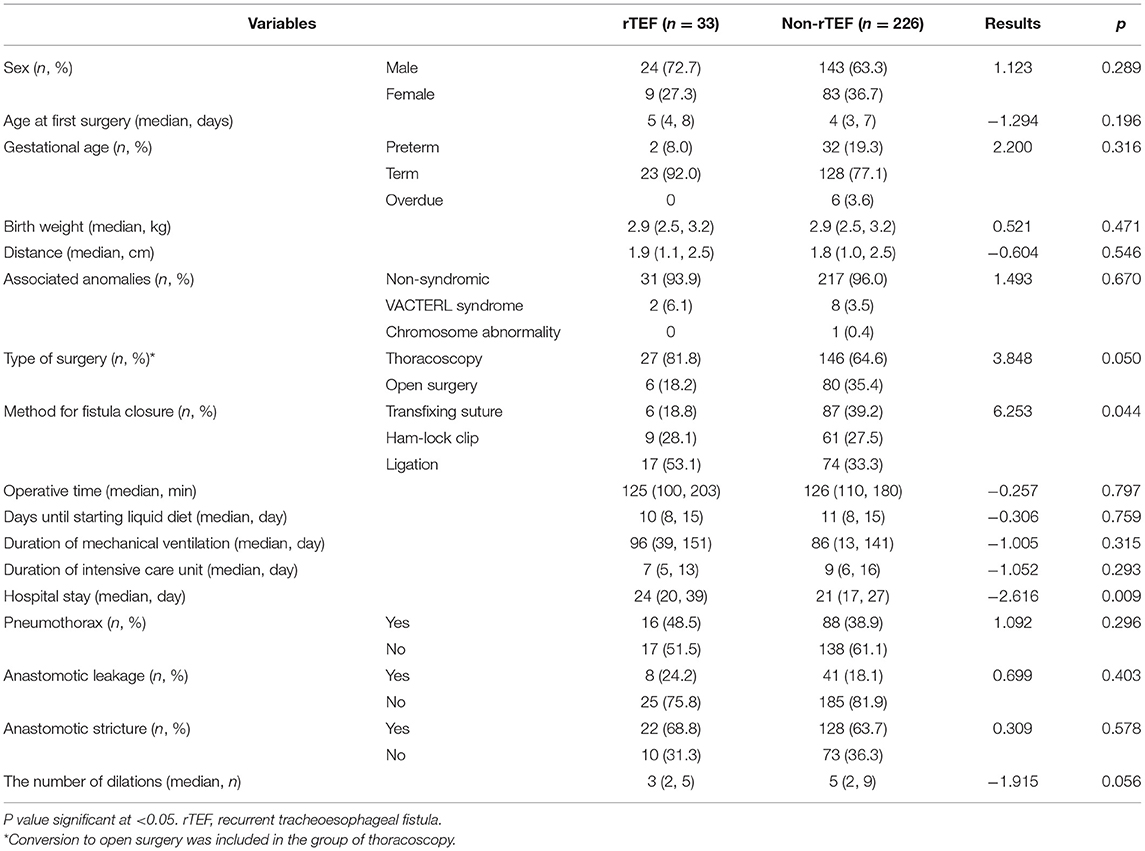
Few studies have reported the influencing factors of TEF. According to previous reports, TEF may be associated with premature delivery, low birth weight (7), anastomotic leakage, anastomotic stricture (8, 9), and continuous esophageal dilation (2). Vered et al. reported that patients with TEF had significantly more hospitalizations for respiratory symptoms and significantly more episodes of clinical bronchiolitis. In addition, the patients with TEF had markedly more episodes of positive polymerase chain reaction for viruses (10). In this study, we found that TEF was associated with the method for original fistula closure and the length of hospital stay. Other clinical features, perioperative conditions, and postoperative complications of EA/TEF were not significantly correlated with the occurrence of TEF.
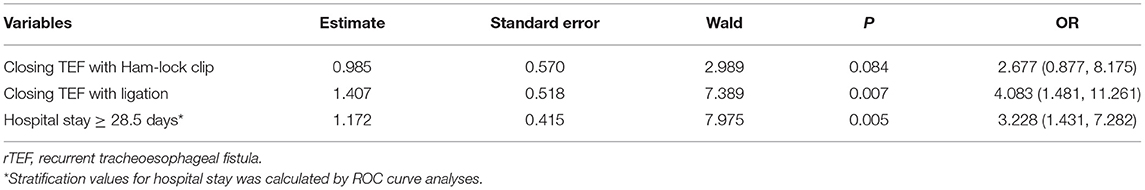
There is no unanimity on the fistula closure technique for the primary repair of EA/TEF. In our research, the method of fistula closure has evolved from ligation to Ham-lock clip and then to transfixing suture. During thoracotomy, we use ligation (n = 4) or sutures (n = 80) to close the fistula. Ligation is used to ligate, and suture is used to transfix the tracheal end of the fistula, both of which occur before eventually cutting the fistula off. For thoracoscopic surgery, we use ligation (n = 86), ham-lock clips (n = 70), or sutures (n = 10) to close the fistula. The use of ligation and sutures is the same as during thoracotomy. The Ham-lock clip is used to clip and close the fistula near the trachea before cutting it off. We found that separating the fistula after ligation was an important risk factor for recurrence. In early EA/TEF repair, the fistula was simply ligated and an esophagus end-to-side anastomosis was performed, but it was believed that the fistula may be recanalized after surgery (11). Subsequently, surgeons tended to double-ligate and divide the fistula instead, followed by an end-to-end esophagus anastomosis. The incidence of TEF after surgery ranges from 3 to 22% (12). Closing the fistula with transfixing suture can effectively reduce the incidence of TEF. The European Reference Network for Rare Inherited Congenital Anomalies (ERNICA) Consensus Conference on the management of patients with EA/TEF recommends the use of sutures to close the fistula (13). Previous research believed that there is an obvious risk of migration of the clip through the wall of the fistula and the development of a recurrent fistula (14), but our results show that using a Ham-lock clip to close the fistula is not a risk factor for TEF. Schlesinger et al. (15) reported usage of surgical clips to close the fistula in 67 patients, and only two patients subsequently developed TEF. Nonetheless, the safety and effectiveness of surgical clips need further research before widespread clinical application.
We found that the length of hospital stay during the primary repair of EA/TEF was significantly longer in patients with TEF than that of patients without TEF. Although postoperative complications such as anastomotic leakage, pneumothorax, and anastomotic stricture were not significant risk factors of TEF in this study, abscess formation, pneumonia, and the above complications may prolong hospital stay. Furthermore, premature is also associated with longer hospital stays (Supplementary Table 1). Therefore, a prolonged hospital stay is a comprehensive reflection of postoperative complications and the recovery process. Due to the limitations of retrospective study case records, this study did not include abscess formation and pneumonia as factors; further research should be carried out for better understanding.
Due to the high proportion of recurrence of TEF after TEF repair, the intraoperative skills and perioperative management of TEF repair are very important. The technique currently adopted by our hospital is to use an absorbable 5-0 monofilament thread to sew up and close the tracheal end of the fistula before cutting the fistula off. Both incised ends of the fistula are then respectively closed using three interrupted 5-0 sutures (the tracheal end of the fistula is sutured twice to ensure that it is closed completely and to prevent air from escaping). Finally, the free part of the prevertebral fascia is placed between the two ends of the fistula to isolate the ends, which is known to prevent re-recurrence of the fistula. At present, it is generally believed that it is very important to choose a suitable tissue liner between the incised TEF during the TEF operation to improve the success rate and avoid recurrence. Whether the application of this technique can reduce the occurrence of TEF is still worthy of future research.
Basing on this is retrospective study, surgical procedures and details, and perioperative management will change over time, and access to surgical details and postoperative complications information is also limited. Surgery performed by different surgeons and the respective follow-up time is different, resulting in a certain degree of heterogeneity in the results. Due to the small sample size of the two centers, the conclusions cannot be verified externally. We need to prospectively recruit more patients for regular and longer follow-up and obtain more detailed surgery and perioperative records to further understand the long-term prognosis of these patients and analyze risk factors for TEF.
In conclusion, using transfixing sutures to close TEF is an important protective factor for TEF. We should avoid simply ligating the fistula during the primary repair of EA/TEF. Furthermore, patients with long postoperative hospital stays (≥ 28.5 days) and postoperative complications should be highlighted for the possibility of TEF during follow-up.